概述
一颗二叉搜索树可以为空,但如果不为空,必须满足以下性质:
- 非空左子树的所有键值小于其根结点的键值
- 非空右子树的所有键值大于其根结点的键值
- 左、右子树都是二叉搜索树

二叉查找树代码
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root; // 二叉查找树的根结点
private class Node{
private Key key; // 键
private Value val; // 值
private Node left, right; // 指向子树的链接
private int size; // 以该结点为根的子树中的结点总数
public Node(Key key, Value val, int size) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.size = size;
}
}
.
.
.
}
二叉查找树操作
查找操作
在二叉查找树中查找一个键的递归算法:如果树是空的,则查找未命中;如果被查找的键和根结点的键相等,查找命中,否则我们就(递归地)在适当的子树中继续查找。如果被查找的键较小就选择左子树,较大则选择右子树。

代码
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
// 在以 x 为根结点的子树中查找并返回 key 所对应的值
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls get() with a null key");
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return get(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) return get(x.right, key);
else return x.val;
}
插入操作
插入方法的实现逻辑和递归查找很相似:如果树是空的,就返回一个含有该键值对的新结点;如果被查找的键小于根结点的键,我们会继续在左子树中插入该键,否则在右子树中插入该键。
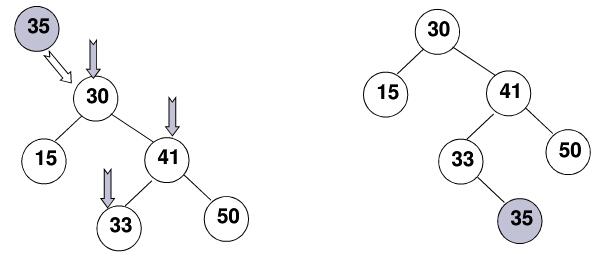
代码
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
root = put(root, key, val);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
// 如果key存在于为根结点的子树中则更新它的值
// 否则将以key和val为键值对的新结点插入到该子树中
if (x == null) return new Node(key, val, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
else x.val = val;
x.size = 1 + size(x.left) + size(x.right);
return x;
}
查找最小值和最大值
最小元素一定是在树的最左分支的端结点上;最大元素一定是在树的最右分支的端结点上。
// 最小值查找
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x;
else return min(x.left);
}
// 最大值查找
public Key max() {
return max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) return x;
else return max(x.right);
}
删除操作
deleteMin() 删除最小键
二叉查找树最难实现的方法就是 delete() 方法。作为热身运动,我们先考虑 deleteMin() 方法。最小键只能在左子树的端结点上,所以删除最小键 deleteMin 仅有以下两种情况。如下图所示,最小键就是 15 这个结点,它有两种情况:15 下面无子结点,15 下面有一个子结点(右子结点)。
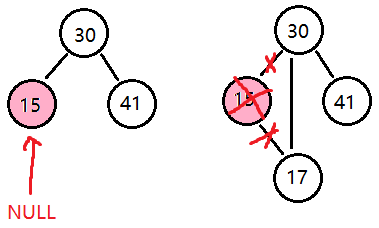
这两种情况的删除操作是非常容易实现的:若被删除结点无子结点,仅需将其置为 NULL 即可;若被删除的结点有一个子结点,仅需将其父结点指向其子结点即可,此时已经没有任何链接指向被删除的结点,因此它会被垃圾收集器清理掉。
代码
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
注意:deleteMax 和 deleteMin 是同理,所以就不再说明了。
delete() 删除操作
有了 deleteMin 操作的启示,我们可以用类似的方式删除任意只有一个子结点(或没有子结点)的结点,但应该怎样删除一个拥有两个子结点的结点呢?如下图所示。
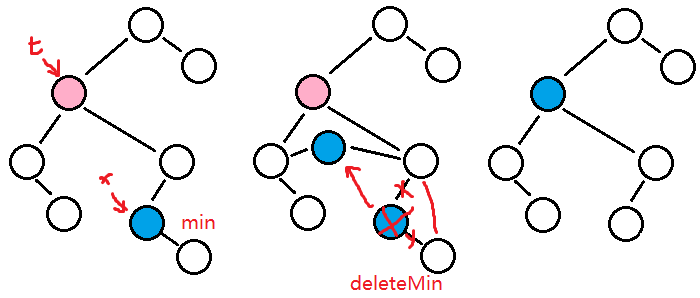
思路如下:
- 先找到被删除结点 t,再找 t 的右子树中最小结点或左子树最大结点 x,此案例是找右子树最小结点,用 min 实现
- 将 x 与 t 调换,t 位置就被 x 代替了,并仅需删除 x 原位置即可。这么做的好处是,由删除 t,变成了删除 x,而 x 是最小结点,所以仅一个或无子结点,此时删除操作就简单了,deleteMin 实现即可。
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left; // 一个或无子结点情况
if (x.left == null) return x.right; // 一个或无子结点情况
// 两个子结点情况
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right);
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; // 更新结点计数器
return x;
}